- Shanghai Zhongshen International Trade Co., Ltd. - Two decades of trade agency expertise.
- Service Hotline: 139 1787 2118
ChinaphotovoltaicThe industrys rapid expansion has garnered widespread global attention and is expected to significantly impactsolarcomponent supply chains in the coming years. According to the latest report from Wood Mackenzie, how will this trend shape the future landscape of the global photovoltaic market? Below is an in-depth analysis of this issue.
I. Expansion of Chinas Photovoltaic Industry
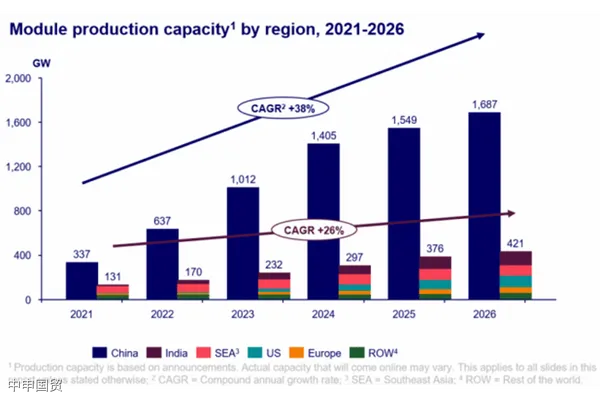
China is projected to invest over $130 billion in its domestic solar industry between 2023 and 2026. By 2024, China is expected to possess over 1 TW of wafer, cell, and module capacity—sufficient to meet global annual demand from now until 2032. This expansion is primarily driven by high polysilicon profits, technological upgrades, and policy support, enabling China to dominate the global solar supply chain while widening its technological and cost advantages over competitors.
II. Impact on Global Supply Chains
Despite overseas governments efforts to promote local solar manufacturing growth, their costs remain uncompetitive compared to Chinese supply. Chinese-made modules are priced significantly lower than those from Europe and the U.S. Overseas markets like the U.S. and Europe, lacking key upstream raw material capacity, cannot compete with China on price for domestically produced modules. Additionally, while the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act and Indias Production-Linked Incentive scheme aim to expand module capacity, both countries will remain reliant on Chinese wafer and cell supplies in the short term.
III. Future Market Competition
Market oversupply and intense competition will characterize the future solar supply chain. Demand for P-type cell production lines is expected to decline starting in 2023, dropping to just 17% of supply by 2026—necessitating upgrades or phased shutdowns. Meanwhile, cell manufacturing capacity expansion is projected to outpace wafers and modules, making cells the most competitive segment in the module supply chain. India, due to its strong incentive policies, is expected to become the worlds second-largest module producer by 2025.
In summary, Chinas photovoltaic industry expansion will significantly impact global supply chains in the coming years. Chinese manufacturings price advantages and technological leadership will make it difficult for overseas markets to reduce reliance on Chinese wafers and cells. Simultaneously, market oversupply and technological upgrades will usher the photovoltaic industry into a more challenging era.
Related Recommendations
Category case
Contact Us
Email: service@sh-zhongshen.com
Related Recommendations
Contact via WeChat

? 2025. All Rights Reserved. Shanghai ICP No. 2023007705-2  PSB Record: Shanghai No.31011502009912
PSB Record: Shanghai No.31011502009912








