- Shanghai Zhongshen International Trade Co., Ltd. - Two decades of trade agency expertise.
- Service Hotline: 139 1787 2118
With growing public attention to health, the health food market has become increasingly active, emerging as a hotspot in global trade. In this sector, Canada is an important trade partner for China. The cooperation potential between China and Canada in health foods is vast, but to successfully enter the Canadian market, Chinese companies must understand and comply with a series of regulations and standards, preparing comprehensive documentation to meet Canadas market access requirements.
I. Regulatory Authorities and Systems
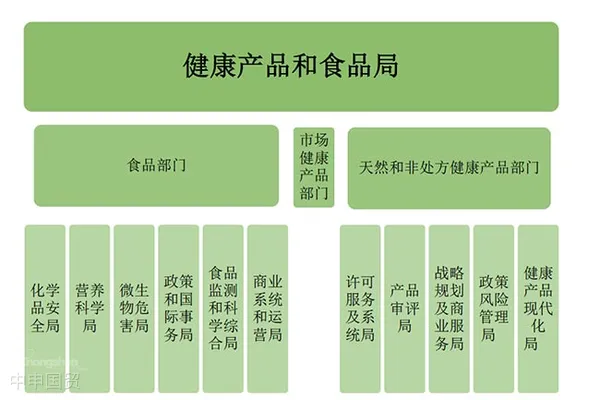
In Canada, health food-like products are mainly categorized into two types: Natural Health Products (NHPs) and Nutrition products. Health Canada is the federal department responsible for public health, with the Health Products and Food Branch overseeing these two categories. The Natural Health Products Directorate (NHPD) specifically handles the stringent approval and regulation of NHPs.
Health Canadas organizational structure is rigorous, with clearly defined responsibilities across departments, forming a comprehensive management and regulatory system that ensures the safety and efficacy of health foods sold in Canada.
II. Legal and Regulatory Framework
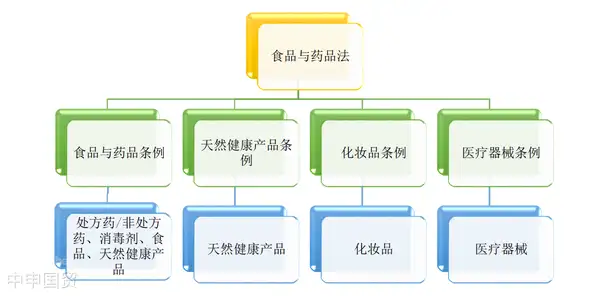
Canadas food legal and regulatory framework is well-structured, primarily consisting of three levels: Acts, Regulations, and Guidance documents. Acts are enacted by the Canadian Parliament and represent the highest level of the regulatory framework. Regulations are issued by departments designated under the Acts, providing further details and specifying procedures and requirements. Guidance documents are advisory opinions from specific regulatory bodies on particular matters and are not legally binding.
Key regulations governing Natural Health Products include the Food and Drugs Act (FDA), the Natural Health Products Regulations (NHPR), and related guidance documents. These laws and regulations provide strict standards and guidance for the production, sale, and management of NHPs, ensuring product quality and safety.
III. Product Market Entry Requirements
Product Definition
Natural Health Products in Canada are typically derived from plants but may also come from animals, microorganisms, and marine sources. These products include vitamins and minerals, herbal remedies, homeopathic medicines, and traditional medicines. Many everyday consumer goods, such as certain toothpastes, antiperspirants, shampoos, facial products, and mouthwashes, are also classified as NHPs in Canada.
Nutrition products in Canada fall under the food category and are generally regulated similarly to food, but they can apply for health claims on labels.
Market Access Requirements
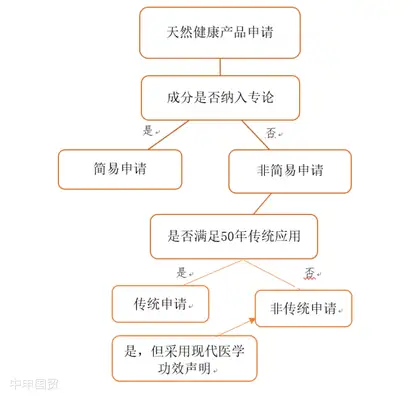
Canada implements a stringent approval system for NHPs. Before entering the market, products must submit extensive reports and experimental data, providing complete information on ingredient names, sources, dosages, functional claims, and recommended usage. They must also obtain an 8-digit Natural Product Number (NPN) issued by Health Canada for production and sale. Products manufactured in third countries require an import license and must demonstrate full compliance with Canadas Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) requirements.
Market access applications for NHPs consist of two parts: product applications (for product marketing authorization) and site applications (for production and import site authorization). For product applications, if the products ingredients are listed in the Compendium of Monographs published by Health Canadas Natural Health Products Directorate, a simplified application process applies. Otherwise, a non-simplified application is required. Additionally, there are transitional applications and homeopathic applications.
Product Claims
Claims for natural health products and nutritional supplements mainly include health claims, functional claims, general health claims, and nutritional function claims. Among these, health claims refer to any statement, display, or implication on labels or advertisements that suggests a relationship between consuming a certain food and health. In Canada, such claims require approval from Health Canada before they can be used. Currently, Health Canada has approved 16 health claims.
Product Ingredients
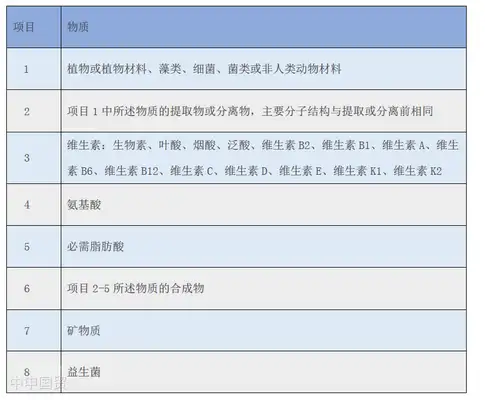
Health Canada has established a separate database for natural health product ingredients, which includes thousands of ingredients such as vitamins, minerals, amino acids, essential fatty acids, probiotics, and herbal plants.
Product Labeling Requirements
Canada has a specific guidance document for the labeling of natural health products—the Labeling Guidance Document. According to this document, the principal display panel of a product must include information such as the brand name, product number, dosage form, and net weight. Additionally, it must specify the name and address of the brand holder, the name and address of the importer, the common and proper names of the product ingredients, the ingredient content and international units, recommended usage purpose, recommended route of administration, recommended dosage, recommended usage time, risk information, recommended storage conditions, and batch number.
When Chinese companies export health products to Canada, they need to understand and comply with relevant Canadian regulations and standards, preparing sufficient documentation to meet market access requirements. Canada has a strict regulatory and legal framework for health food-like products, with clear specifications covering product definitions, market access requirements, product claims, and labeling requirements. Therefore, Chinese companies must thoroughly prepare to ensure their products meet Canadian requirements to successfully enter this market with significant potential.
Related Recommendations
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. Shanghai ICP No. 2023007705-2  PSB Record: Shanghai No.31011502009912
PSB Record: Shanghai No.31011502009912










